+919790726189

This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
PERIAPICAL CYST SURGERY AT WEST MAMBALAM ASHOK ...
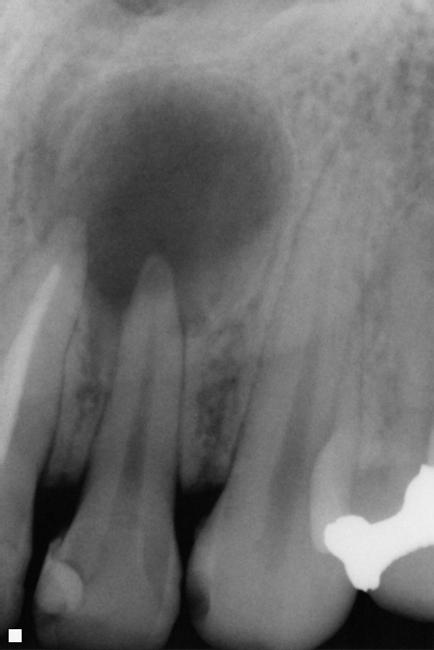
PERIAPICAL CYST SURGERY AT WEST MAMBALAM ASHOK NAGAR CHENNAI Periapical Cyst: Causes, Symptoms, and Management A periapical cyst, also known as a radicular cyst, is the most common type of cyst found in the jaw. It forms at the apex (tip) of a tooth's root as a result of chronic infection or inflammation, typically following tooth decay or trauma. Although generally asymptomatic, these cysts can lead to complications if left untreated, including pain, swelling, and damage to surrounding bone and teeth. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of periapical cysts is crucial to preventing long-term dental issues. What Causes a Periapical Cyst? A periapical cyst develops as a response to infection. When a tooth becomes decayed or is injured, bacteria can enter the pulp (the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels). This infection can lead to the death of the pulp, causing an inflammatory response at the root tip. Over time, the body attempts to isolate the infection by forming a cystic sac filled with fluid, composed primarily of dead cells and tissue debris. Periapical cysts are commonly associated with: Untreated dental caries (tooth decay) Trauma to the tooth (such as a fracture or deep crack) Failed root canal treatments Long-standing untreated infections Symptoms of Periapical Cyst In the early stages, a periapical cyst often goes unnoticed, as it is asymptomatic and grows slowly. It is frequently discovered during routine dental X-rays. However, if the cyst enlarges, it may start causing symptoms such as: Swelling around the affected tooth or in the surrounding gums Pain or discomfort, especially when pressure is applied to the area Sensitivity to touch, temperature, or pressure Pus drainage from the gums, indicating an abscess Discoloration of the affected tooth Loosening of the tooth due to loss of supporting bone Diagnosis To diagnose a periapical cyst, a dentist or endodontist will typically begin with a clinical examination, noting any signs of infection or swelling. However, the definitive diagnosis is made using imaging techniques such as dental X-rays, where the cyst appears as a radiolucent (dark) area around the tip of the tooth's root. In some cases, additional diagnostic tools like a cone-beam CT (CBCT) scan may be used for a more detailed assessment, especially if surgical intervention is required. Management of Periapical Cyst The treatment for a periapical cyst depends on the size of the cyst, the condition of the tooth, and whether the infection has spread to surrounding tissues. Common treatment options include: Root Canal Treatment (RCT) Root canal therapy is the most common and effective treatment for a periapical cyst. The procedure involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth, cleaning and disinfecting the root canals, and sealing them to prevent further infection. In most cases, this treatment helps reduce the size of the cyst, and it eventually heals on its own. Apicoectomy If the cyst persists after root canal treatment or if it is too large, an apicoectomy (root-end surgery) may be performed. This involves making a small incision in the gum to access the cyst and root tip. The infected tissue is removed, and the root end is sealed. Tooth Extraction If the tooth is severely damaged or the infection cannot be controlled, extraction may be necessary. Once the tooth is removed, the cyst is cleaned out, and the area is allowed to heal. Cyst Enucleation In cases where the cyst is particularly large, surgical removal of the entire cyst may be necessary. This is known as cyst enucleation. It ensures complete removal of the cystic lining and reduces the risk of recurrence. Prevention The best way to prevent periapical cysts is by maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking prompt treatment for dental issues. Regular dental checkups allow early detection of tooth decay, infection, or any abnormalities that may lead to cyst formation. Early intervention can prevent the need for more extensive procedures later on. Conclusion A periapical cyst is a manageable condition when detected early. With timely treatment like root canal therapy or minor surgical intervention, most patients can avoid complications such as tooth loss or further bone damage. Regular dental visits and proper oral care are key to preventing the progression of dental infections into more serious problems like periapical cysts. Dental Clinics in West Mambalam Dentists in West Mambalam Dentists in Ashok Nagar Best dentist near me Best Dental Clinics in West Mambalam Oral surgeon in West Mambalam Dental Implants in West Mambalam Oral surgeon in Ashok Nagar

