+919790726189

This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
Congenitally Missing Anterior Teeth: Causes, Im...
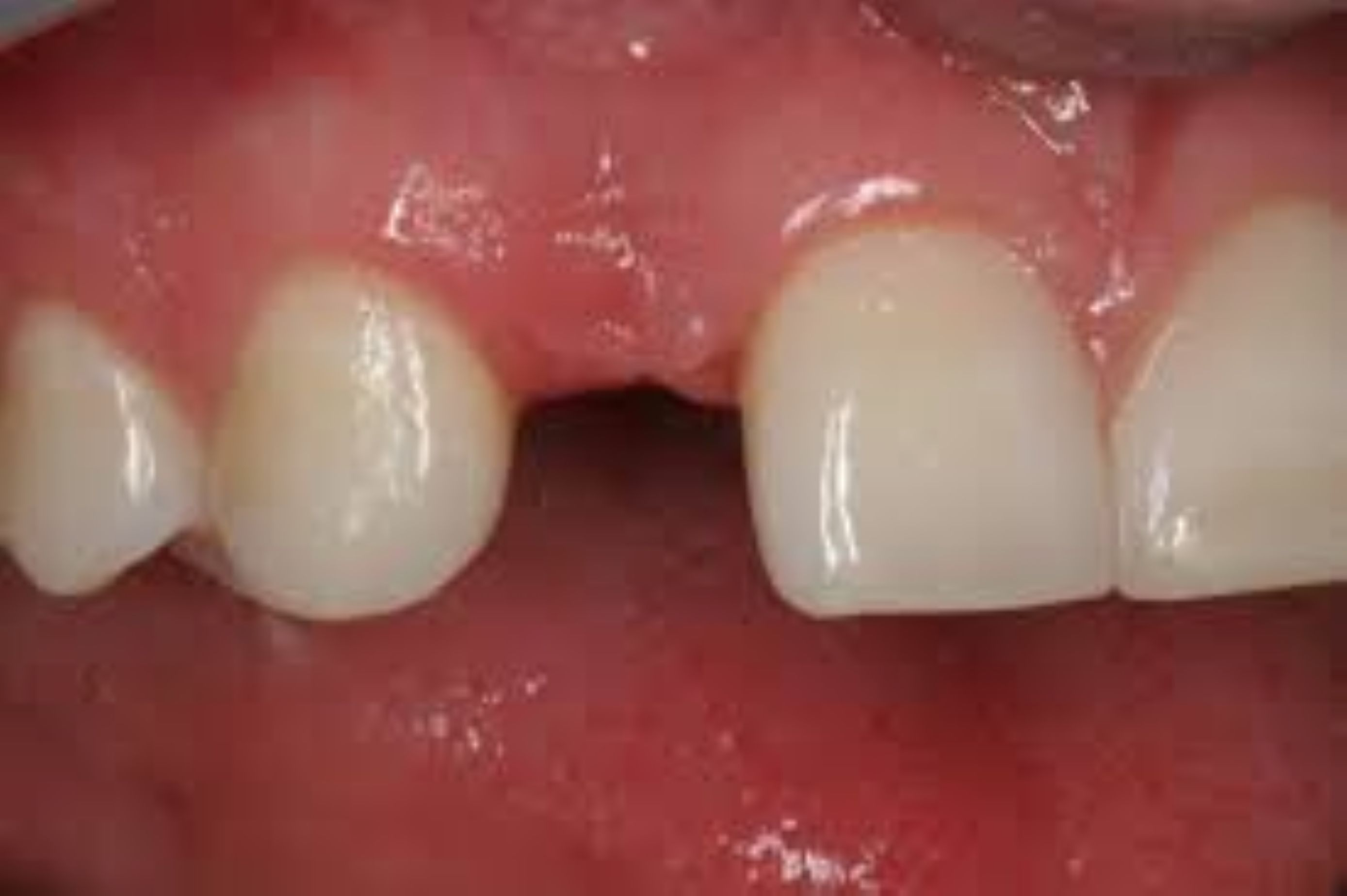
Congenitally Missing Anterior Teeth: Causes, Impact, and Treatment Options Congenitally missing anterior teeth, also known as hypodontia, is a dental anomaly where one or more front teeth fail to develop during childhood. This condition can affect both the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) arches, with the lateral incisors being the most commonly missing anterior teeth. While it can affect both primary and permanent teeth, the permanent dentition is more often impacted. Causes The causes of congenitally missing anterior teeth are typically genetic. It often runs in families and is associated with certain syndromes such as ectodermal dysplasia and Down syndrome. However, in many cases, it occurs in individuals without any associated syndromic conditions. Environmental factors during pregnancy, such as infections, trauma, or exposure to harmful substances, may also play a role, though less commonly. Clinical Implications The absence of anterior teeth, especially in the aesthetic zone, can have significant functional, psychological, and social impacts. These include: Aesthetic concerns: Missing front teeth can affect smile appearance and facial symmetry, especially in young individuals. Speech difficulties: Anterior teeth play a role in pronunciation, especially for sounds like "s" and "th". Bite problems: The absence of teeth may cause adjacent teeth to shift, leading to malocclusion. Bone loss: Lack of tooth development may result in poor alveolar bone growth in the affected region. Early diagnosis is essential. Pediatric dentists or orthodontists can detect missing anterior teeth by the age of 7 or 8 using clinical exams and radiographs. Treatment Options Treatment of congenitally missing anterior teeth depends on the patient's age, number of missing teeth, spacing, bone condition, and overall oral health. Some common approaches include: Orthodontic space closure: Braces or aligners may be used to close gaps by moving adjacent teeth into the missing space. This is common when lateral incisors are missing and canines are moved into their place. Space maintenance and prosthetic replacement: If orthodontic closure is not viable or desired, space is maintained for future tooth replacement options such as: Dental implants: A permanent and aesthetic solution, ideal once jaw growth is complete (usually after age 18). Resin-bonded bridges (Maryland bridges): A conservative fixed prosthesis suitable for young patients. Removable partial dentures: Often used as a temporary measure in growing children. Restorative reshaping: In some cases, reshaping or bonding canines to resemble lateral incisors can be done for better aesthetics. Conclusion Congenitally missing anterior teeth present both aesthetic and functional challenges, but with timely diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach involving pediatric dentists, orthodontists, and prosthodontists, excellent outcomes can be achieved. Early intervention ensures proper oral development, confidence, and long-term dental health. Dental Clinics in West Mambalam Dentists in West Mambalam Dentists in Ashok Nagar Best dentist near me Best Dental Clinics in West Mambalam Oral surgeon in West Mambalam Dental Implants in West Mambalam Oral surgeon in Ashok Nagar Painless tooth removal at West Mambalam Rootcanal treatment at West Mambalam Top rated dentist in West Mambalam

